About Israel and Palestine
Israel and Palestine are two separate political entities in the Middle East, with Israel being a sovereign country and Palestine being a partially recognized state. The conflict between the two is centred on issues such as borders, security, and control of Jerusalem, and has a long history dating back to the 20th century.
The conflict between Israel and Palestine is often referred to as the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It has its roots in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when Jewish immigration to Palestine, then part of the Ottoman Empire, increased. Following the collapse of the Ottoman Empire after World War I, the British took control of Palestine and implemented policies that favoured Jewish immigration and settlement. After World War II, tensions between Jews and Arabs in Palestine escalated, leading to the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948 and the first Arab-Israeli war. Since then, the conflict has continued, with periods of violence and attempts at peace negotiations. The current situation is characterized by Israeli military control in the West Bank and the blockade of the Gaza Strip by Israel, which has been criticized by many for causing humanitarian suffering.
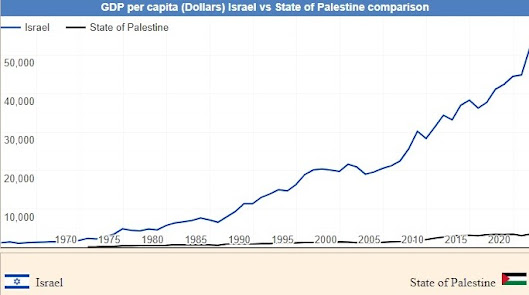
Israel has a developed economy with a high standard of living, while Palestine has a struggling economy with limited self-governing authority, primarily due to ongoing conflict and restrictions imposed by Israel. The Palestinian economy is heavily dependent on foreign aid and faces challenges such as high unemployment and limited access to resources and markets. Israel has a strong economy with a high GDP, while Palestine has a weaker economy with a much lower GDP. The Palestinian economy is heavily dependent on foreign aid and faces challenges such as limited access to resources and markets, which are partially due to the ongoing conflict and restrictions imposed by Israel. Nevertheless, there have been some efforts to improve the Palestinian economy, such as through foreign investment and the development of natural resources.
Israel and Palestine are two separate political entities in the Middle East, each with its own distinct characteristics,
01. Israel: A sovereign country located in the eastern Mediterranean, recognized as a state by most of the international community. It has a developed economy, a democratic political system, and a strong military.
02. Palestine: A partially recognized state, claimed by the Palestinian National Authority (PNA), which exercises limited self-rule in parts of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. It has a struggling economy and a limited self-governing authority, and its political status is a central issue in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
03. Population: Israel has a predominantly Jewish population, with minority populations of Arabs, Christians, and others. The Palestinian territories have a predominantly Palestinian Arab population.
04. Political systems: Israel is a parliamentary democracy with a prime minister as its head of government. The Palestinian territories have a limited self-governing authority, with a president as its head of state.
05. Relations with other countries: Israel has diplomatic relations with most countries, while Palestine's international recognition is limited. The recognition of Palestine as a state by some countries has been a source of diplomatic tension.
Why are Israel and Palestine conflicted?
The conflict between Israel and Palestine is a complex and deeply ingrained issue, and there is no easy solution. Efforts to resolve the conflict have included diplomatic negotiations, agreements, and peace processes, but so far, a lasting peace has not been achieved. Some steps that could be taken to help resolve the conflict include:
01. Direct negotiations: Both parties need to engage in direct and meaningful negotiations to address the core issues of the conflict, including borders, the status of Jerusalem, and the rights of Palestinian refugees.
02. End to violence: An end to violence and acts of terrorism by both sides is necessary for any peace process to be successful.
03. Addressing the humanitarian crisis: The international community must address the humanitarian crisis in the Palestinian territories, including the lifting of the Israeli blockade of the Gaza Strip.
04. Improving economic conditions: Improving the Palestinian economy through investment and development could help create a more stable and secure environment for peace negotiations.
05. International support: The international community, including the United Nations, the United States, and the European Union, should support efforts to resolve the conflict and act as mediators and facilitators in negotiations.
These steps alone will not guarantee a resolution, but they could help create a more conducive environment for peace negotiations and a lasting solution to the conflict.
Why are humans make violence?
Human violence is a complex and deeply ingrained issue that has been present throughout history. There are a variety of factors that contribute to human violence, including psychological, social, cultural, and economic factors. From a psychological perspective, mental health problems, such as anger, aggression, and impulse control disorders, can contribute to violent behavior. In some cases, individuals with a history of trauma or abuse may engage in violent behavior as a coping mechanism or as a way to exert power and control over others.
Social and cultural factors also play a role in human violence. The influence of family, peers, and the media can shape attitudes and beliefs about the use of violence, and cultural norms and values can condone or reject the use of violence in different situations. For example, some cultures may view violence as an acceptable means of resolving conflicts, while others may view it as unacceptable.
Economic factors, such as poverty and inequality, can also contribute to human violence. In many cases, poverty and unemployment can lead to desperation and a sense of hopelessness, which can in turn lead to violent behavior. Additionally, societal inequalities, such as discrimination and prejudice, can also contribute to violence, as marginalized and oppressed groups may engage in violent behavior as a means of resistance.
In conclusion, human violence is a complex issue with a variety of contributing factors. Addressing these underlying causes is essential for reducing and preventing violence. This may involve addressing mental health needs, changing cultural norms and values, addressing poverty and inequality, and promoting non-violent conflict resolution. By working to understand and address the root causes of human violence, we can create a safer and more peaceful world for everyone.
Thank you,
UBApepi team













1 Comments
👍😏
ReplyDelete